In recent years business has changed dramatically but keeping your sites, people, and vehicles safe will always be a priority to any company.
With more and more businesses turning to more contemporary methods of security, we will be taking a look at one of the most straightforward and effective methods, Key Fobs.
In this simple guide, we will take a look at Key Fob Access Control, how it works, some of the benefits, key elements, and industries that can utilise these types of systems.
- An overview of Key Fob Access Control
- Features of Key Fob Access Control
- How Key Fob Access Control works
- Key Fob Access Control benefits
- Industries who can use Key Fob Access Control
What is Key Fob Access Control?
Despite what most people think, Key Fob systems have been around since the early 80s and have been popular since their inception.
However, these systems have come a long way from there. Primarily used for cars and using line of sight infrared technology, the early versions of the system were fairly flawed and easy to copy.
Nowadays, a Key Fob Access Control system is highly secure and uses different technology such as passive radio frequency (RFID), Bluetooth, or Near Field Communication (NFC).

Traditional lock and keys are being phased out in a lot of different industries and keyless entry, tap-to-pay, and fob technology is being seen more and more in our everyday lives.
This shift away from lock and key has occurred due to a few factors, such as technological advances, security flaws of traditional systems, and increased internal threats.
Whether it’s paying for your coffee with a contactless card, accessing a car without a key, or opening a door at work, we have probably seen more of this technology than we think. The prevalence of Key Fob technology is only set to expand in the coming years.
Key Fob systems basically allow a fob (often a credit card size transmitter) to communicate with the receiver (in a door or lock), to unlock and give access to a building, area, or vehicle.
How does Key Fob Access Control work?
Key Fob Access Control systems are fairly straightforward and utilise short-range communication between two devices to unlock doors, locks, vehicles, and more.
In more technical terms, these Key Fobs use RFID (a type of radio frequency), which is a form of barcode system that transfers data using electromagnetic fields and communicates this data to the system from the fob using radio waves.
Unlocking a door or lock using a Key Fob is as simple as holding your fob in front of the reader, which will read the microchip in your fob and open the door or lock.
Customisable access means that you can limit certain people to different areas that relate to their work. For example, the custodian, cleaner, or janitor might have full access, whereas a receptionist would only need limited access.
Technical Aspects of Key Fob Access Control Systems
Ever wondered what makes key fob access control systems tick?
Let's dive into the technological heart of these security marvels, exploring the intricate details that keep our spaces safe and accessible.
RFID Technology: The Cornerstone of Key Fob Systems
Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) is the unsung hero of key fob access control. But did you know there's more than one type of RFID?
Let's break it down:
- Low-Frequency (LF) RFID:
- Frequency: 125-134 kHz
- Read Range: Up to 10 cm
- Use Case: Ideal for door access in small offices - High-Frequency (HF) RFID:
- Frequency: 13.56MHz
- Read Range: Up to 1 meter
- Use Case: Perfect for larger facilities with higher security needs - Ultra-High-Frequency (UHF) RFID:
- Frequency: 860-960 MHz
- Read Range: Up to 12 meters
- Use Case: Suitable for vehicle access control in parking garages
The choice between these types affects both security and user convenience.
Shorter read ranges offer tighter security but require closer proximity, while longer ranges provide easier access but may be more vulnerable to interception.
Components of an RFID System
- Tag (Key Fob): Contains an antenna and a microchip with a unique identifier
- Reader: Emits radio waves and receives signals from the tag
- Database: Stores information and permissions associated with each tag
Encryption Methods: Keeping Data Under Lock and Key
In the world of access control, encryption is our digital fortress.
Here's how we keep the data secure with Common Encryption Protocols:
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard):
- 128-bit, 192-bit, or 256-bit key lengths
- Widely used due to its robust security and efficiency - 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard):
- Uses three 56-bit keys
- Still in use, though gradually being phased out in favor of AES
Rolling Codes: A Moving Target for Hackers
Rolling codes, also known as hopping codes, change the key fob's code after each use. This clever trick prevents replay attacks where a hacker might try to use a previously intercepted code.
End-to-End Encryption: No Weak Links
From the moment your key fob communicates with the reader to when the data reaches the central system, end-to-end encryption ensures that your information remains scrambled and useless to potential interceptors.
Key components of Key Fob Access Control
In this section, we will take a quick look at some of the key components of Key Fob Access Control systems and their practical uses.
How Secure are Key Fob Access Control Systems?
Unique Access Control - limit who can access different areas within your company or sites by only giving access to certain areas to specific individuals or teams, increasing your security.
More Secure than Coded Options - a lot of industries use door/safe codes, the issue with these is that they can be shared, giving access to anyone, whereas a fob is easily trackable and makes the staff more accountable.
Timed Access - you can control not only where people can access, but also when they can access the building, doors, or locks, for example, if someone isn’t at work on the weekend their access can be only on weekdays.
Visitor Privileges - Key Fob Access Control can also grant temporary access to visitors, external stakeholders, or people who need short-term access, such as contractors, freelancers, or maintenance professionals.
How Does Key Fob Access Control Differ From Lock and Key?
Robust Design - with keys there is always a possibility of a lock getting jammed, a key getting lost, or broken in the lock. Key Fobs offer an easy and convenient option that improves your security and limits breaches.
Difficult to Reproduce - technically speaking, you can copy a Key Fob, but it is not a simple process and not one that someone could do without a lot of technical know-how.
Regardless, this is much harder than copying a traditional key which can be done at multiple locations with ease.
System Management - unlike keys, you can manage your system very easily, tracking who has a fob, when they use it, where they have access to, and the ability to reset, deactivate and create new fobs with ease.
Low-Impact Installation - compared to other security systems or traditional locks, implementation of a Key Fob system is fairly rudimentary and means it can be used in a wide range of industries, companies, and locations.
| Feature | Key Fob | Traditional Keys | Keypads | Biometrics |
| Convenience | High - tap or wave | Moderate - Insert and turn | Moderate - Enter Code | High - Use body part |
| Security | High - Encrypted | Low - Can be copied | Moderate - Can be shared | Very High - Unique to individual |
| Ease of Revoking Access | Easy - Deactivate fob | Difficult - Change locks | Easy - Change code | Easy - Remove from system |
| Cost | Moderate | Low | Low to Moderate | High |
| Durability | High | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Tailored Access Levels | Yes | Limited | Yes | Yes |
| Scalability | High | Low | Moderate | High |
| Maintenance Required | Low | Moderate | Low | Moderate |
What are the benefits of Key Fob Access Control?
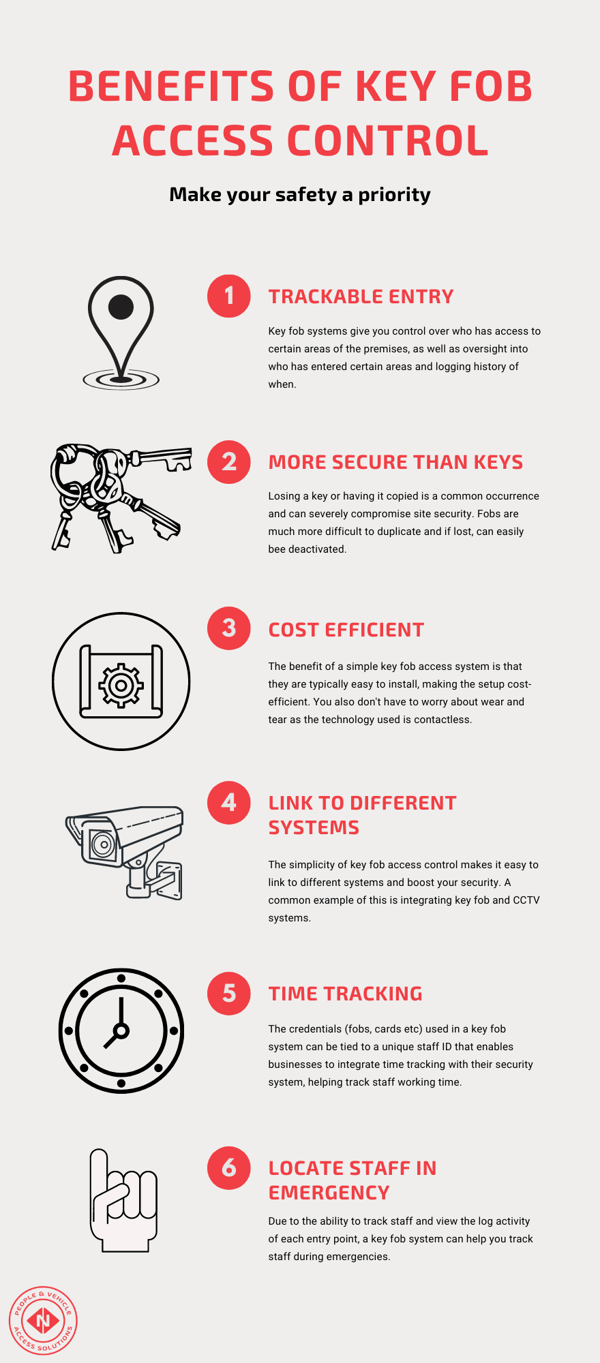
Enhanced Security
- Trackable Entry: Monitor who accesses specific areas and maintain comprehensive entry/exit records.
- Access Limitation: Tighten security by restricting access to authorized personnel only.
- Reduced Internal Shrinkage: Minimise stock loss and internal theft through improved access management.
- Detailed Audit Trails: Easily trace staff movements and door access for improved security management.
- Superior to Traditional Keys: Unlike easily copied or lost keys, fobs offer better security with deactivation options for lost devices.
Streamlined Implementation
- System Integration: Seamlessly integrate with existing security systems for comprehensive protection.
- Cost-Efficiency: Eliminate expenses associated with lock changes and key replacements.
- Minimal Wear and Tear: Contactless technology (NFC, Radio, Bluetooth) reduces mechanical degradation.
- Multi-System Compatibility: Link with other security measures like CCTV for enhanced verification.
Operational Advantages
- Dual-Purpose Functionality: Fobs can double as ID cards, improving accountability and identification.
- Emergency Location Tracking: Quickly locate staff during emergencies through access records.
- Automatic Locking: Ensure consistent security with auto-locking features upon door closure.
The versatility of key fob access control systems offers numerous benefits across various industries and organisation sizes. As you explore this technology, you may discover additional advantages tailored to your specific needs.
What industries can benefit from Key Fob Access Control?
Key Fob Access Control remains one of the best ways to secure your business which is not only cost-effective, but simple to set up and use.
Let's explore how different industries leverage this technology to enhance safety, efficiency, and user experience.Education: Nurturing Minds in a Safe Environment
Educational institutions face the dual challenge of fostering an open learning environment while ensuring student and staff safety. Key fob access control provides an elegant solution.- Building Access Management: Schools use key fobs to control access to different buildings or areas based on student year, faculty department, or administrative roles.
- Enhanced Campus Security: With key fobs, security teams can quickly lock down buildings in emergency situations, significantly improving response times.
- Multifunctional Integration: Many institutions integrate key fobs with library systems for book checkouts or cafeteria systems for meal plan management, creating a seamless student experience.
Manufacturing: Enhancing Safety and Productivity
In manufacturing environments, key fob access control systems play a crucial role in maintaining safety standards and optimising workflows.
- Zoned Access Control: Different production areas can be assigned varying access levels, ensuring employees only enter areas relevant to their roles.
- Time and Attendance Tracking: Key fobs double as time clocks, accurately recording shift start and end times, breaks, and overtime.
- Safety System Integration: Access control can be linked with safety systems, preventing untrained personnel from entering hazardous areas or operating dangerous machinery.
Residential Complexes: Combining Convenience and Security
Key fob systems are increasingly popular in residential settings, offering a perfect blend of security and ease of use.
- Seamless Access: Residents can easily access common areas, parking garages, and their individual units with a single fob.
- Visitor Management: Some systems allow residents to grant temporary access to visitors via a mobile app linked to the key fob system.
- Smart Home Integration: Advanced key fob systems can interface with smart home features, activating personalised settings as residents enter their units.
By tailoring key fob access control systems to the unique needs of each industry, businesses can significantly enhance security, streamline operations, and improve user experiences.
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications of key fob access control across various sectors.

